Data Structure :-
It is a critical part of data management. A data structure is a
basically a group of data elements that are put together under one name and
which defines a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer, so
that it can be used efficiently.
In other words we can say that , Data
structure is a representation of the logical relationship existing between
individual elements of data and it is the way of organizing all data item that
consider not only the element stored but also there relationships to each
other.
Classification of Data Structure:-
Two classes of data structure are use in
data structuring:-
·
Primitive data structure
·
Non Primitive data structure
Primitive data
structure :-
Primitive data structure are integer,
real, character and boolean data type.
Non primitive
data structure:-
Non primitive
data structure are of two type:-
·
Linear data structure
·
Non linear data structure
Linear data
structure :-
Linear data
structure are as follows:-
·
Array
·
Linked list
·
Stack
·
Queue
Non linear
data structure :-
Non linear data
structure are as follows :-
·
Tree
·
Graph
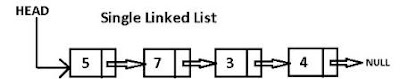
Linked list:-
Linked list are the special type of data element usually structure
that contain a reference to the data of its same type. So it is called self
referential structure. In addition to another data linked list contains a
pointer to a data that is the same type of as that of the structure.
With the help of this pointer data
element links to one another.
Struct link_list
{
Int data;
Struct link_list*next;
} L;
Types of linked list:-
Their are various type of linked list:-
·
Singly linked list
·
Doubly linked list
·
Circular singly linked list
·
Circular doubly linked list
This program is
based on singly linked list.
Singly
linked list:-
A singly linked list is the simple
type of list in which every node contains two parts first is data and
second is a pointer to the next node. A singly linked list allows
traversal of data only in one way.
The first node of
the list is pointed by a pointer which is usually a head or start pointer. The
last node of the list contains NULL value in its pointed field.
Struct linked_list
{
Int data;
Struct linked_list*next;
} node*
Algorithm
to create a linked list
Step 1: [initialize] start=NULL
Step 2: set ptr=start
Step 3:repeat step 4 to 6 while(ptr->! =NULL)
Step 4: allocate memory for ptr
Ptr=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node))
Start=ptr
Step 5: take value for ptr->data=val
Step 6: set ptr=ptr->next
Step 7: end of loop
Step 8: exit
Algorithm
to display a linked list :-
Step 1: [initialize] start=NULL, ptr=NULL
Step 2: ptr=start
Step 3: repeat step 4 to 5 while(ptr! =NULL)
Step 4: print ptr->data
Step 5: set ptr=ptr->next
Step 6: end of loop
Step 7: exit
Algorithm
to insert a node at the end of the linked list :-
Step 1: [initialize] set *start=NULL, *ptr=NULL, *newnode, val
Step 2: ptr=start
Step 3: newnode=(node*) malloc(sizeof(node))
Set
newnode->data=val
Newnode->next=NULL
Step 4: repeat step 5 while (ptr->next! =NULL)
Step 5: set ptr=ptr->next
[end of loop]
Step 6: set ptr->next=newnode
Step 7:exit
In the program we
have to first write the header file of C language that is #include<stdio.h>,
#include<conio.h>. The we declare structure of list by writing
keyword typedef struct list. Which contain two variables one is data of
int type to store value and second is next of struct list type to
store the adders of next node.
Then we write function prototype :-
·
Create of void type to create
a linked list
·
Display of void type to display the list
·
Insert end of void type to insert a node ate end of the list
Then we start our main() which is
known as driver of all the functions. In that we firstly take a variable option
of int type to for the switch, then our loop starts do in
that we firstly print massage for user like enter 1 to create list, 2 to
display list, 3 to insert a node at the end and 0 to exit. Then the user will
give her choice and the switch starts case 1 is to create a list, case
2 is to display a list, case
3 is to insert end and case 0 is to exit. Then our loop
ends by writing keyword while(option! =0)
and bracket get closed.
Then we starts writing the functions
definition.
·
Void create() : to create a list
We first give our first
element in the data part and put NULL at
the next part. Then we start malloc function to take more memory for the new
nodes and put that address in the previous node next part, though which they
are linked to each other until we 999 as a number then it stops taking number
and get exit.
·
Void display() : to display a list
We initialize ptr=start
and starts loop while(ptr! =NULL) and print ptr->data.
·
Void insertend: to insert a new node at the end
We first allocate memory
for new node by malloc function and we user will give a new element. And initialize ptr=start and loop starts while
ptr->next!=NULL if the condition is true it starts increment when the condition
goes false then in the last node next part new node addres gets stores. Through
this new node get inserted.
INSERT A NEW NODE AT THE END PROGRAM
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
typedef struct list
{
int data;
struct list *next;
}node;
node *start=NULL;
void creat();
void display();
void insertend();
void main()
{
int option;
clrscr();
do
{
printf("\n Main Menu");
printf("\n1:Creat list");
printf("\n2:Display list");
printf("\n3:Insert at end");
printf("\n0:Exit\n");
printf("\nEnter your option:-");
scanf("%d",&option);
switch(option)
{
case 1:creat();
printf("\nlinked list created");
break;
case 2:display();
break;
case 3:insertend();
printf("\nNode inserted at end:-");
break;
case 0:
exit(0);
}
}
while(option!=0);
getch();
}
void creat()
{
node *ptr,*newnode;
int num;
printf("Enter data,pres 999 to exit:-");
scanf("%d",&num);
while(num!=999)
{
newnode=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
newnode->data=num;
if(start==NULL)
{
newnode->next=NULL;
start=newnode;
}
else
{
ptr=start;
while(ptr->next!=NULL)
ptr=ptr->next;
ptr->next=newnode;
newnode->next=NULL;
}
printf("Enter another data:-");
scanf("%d",&num);
}
}
void display()
{
node *ptr;
ptr=start;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
printf("\%d->",ptr->data);
ptr=ptr->next;
}
}
void insertend()
{
node*newnode,*ptr;
int num;
newnode=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
printf("enter num");
scanf("%d",&num);
newnode->data=num;
newnode->next=NULL ;
ptr=start;
while(ptr->next!=NULL)
{ ptr=ptr->next; }
ptr->next=newnode;
}

Post a Comment