Introduction to basic commands of kali Linux
Kali linux commands for beginners
Here are the some basics commands which use in kali linux pen-testing O.S kali linux is basically uses by security experts to setup a security circle for there company from different types of cyber attacks .
Some kali linux basic commands are here for a beginner to use kali linux
1.
Date Command –
This command is generally used to
display the system date and time. You can also set a custom date by typing the
below command in your terminal.
Syntax – “date –set=’2 Apr 2018 16:10′
2.
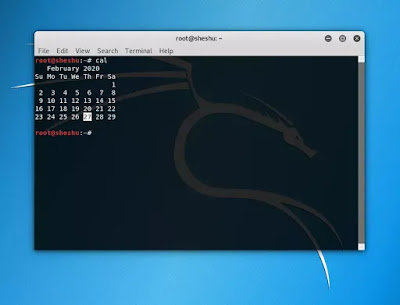
Cal Command –
The cal command simply displays a
formatted calendar of current month in your terminal screen. If in case, you
need an advanced version of cal, then you can also download ncal
package in your Linux machine which displays the calendar vertically along with
more options.
3.
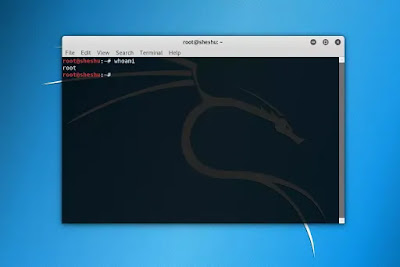
whoami Command –
The whoami command simply
prints the effective user ID where as who command prints the information
about users who are currently logged in.
You can also use the “w”
command to see who is logged on and what they are doing.
4.
pwd Command –
pwd stands for “Print Working Directory” which simply
prints the name of the working directory or you can directly use the below
command to use pwd.
Syntax – “/bin/pwd”
5.
ls Command –
This command is one of the most
useful command in Kali Linux that lists directory contents of files and
directories. With ls command, you can easily list out all hidden files of a
directory with -a attribute and for more detailed output you can
use -l attribute.
Syntax: ls -al
6.
cd Command –
The cd command also known as chdir
(Change Directory) is a command used to change/switch the current working
directory.
7.
mkdir Command –
The command used for creating
directories is mkdir. For example, if you want to create a directory
under Desktop called yeahhub, open a terminal and type the
following command:
Synatx: mkdir /root/Desktop/yeahhub
8.
cat Command –
The cat (concatenate) command is one
of the most frequently used command in Kali Linux which allows us to create
single or multiple files, view contain of file, concatenate files and redirect
output in terminal or files.
Generally, the cat command is used
for displaying the contents of a file.
9.
cp Command –
This command is used to copy files
or group of files or directory which creates an exact image of a file on
a disk with different file name.
10.
mv Command –
The mv command moves, or
renames, files and directories on your file system.
11.
rm Command –
The rm (remove) command is
used to delete files. When used recursively, it may be used to delete directories.
The removal process unlinks a file
name in a file system from its associated data, and marks that space on the
storage device as usable by future writes. In other words, when you remove a
file, the data in the file isn’t changed, but it’s no longer associated with a
filename.
12.
uname Command –
This command prints the information
about the current system. The uname command within Linux allows you to
view system information about your Linux environment.
With uname -a command,
which gives you more information about the system like Kernel Name, Node Name,
Kernel Release, Kernel Version, Machine, Processor, Hardware Platform and
Operating system.
13.
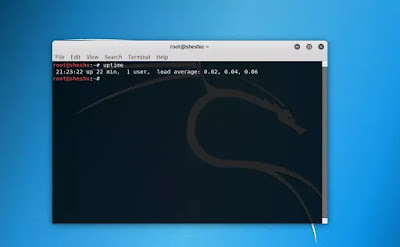
uptime Command –
The uptime command gives you the
time for which the system has been up (or running). Uptime’s basic usage
is very easy – just write the command’s name and press enter.
In case you just want to know the
time for which the system has been up, and that too in a more human-readable
format, use the -p command line option.
14.
users Command –
This command display login names of
users currently logged in on system.
15.
less Command –
less command is used to view files instead of opening the
file. The less command is considered to be a more powerful
version of the “more” command which is used to display information to the
terminal one page at a time.
You can view any text file using the
less command simply by typing the following into a terminal window:
Command: less /etc/passwd
16.
more Command –
The more command allows you to
display output in the terminal one page at a time. This is especially useful
when running a command which causes a lot of scrolling such as the ls command
or the du command.
The more command works with any
application that outputs to the screen. A good way of testing this is to
type the following into a terminal window:
Command: more /etc/passwd
17.
sort Command –
Sort command sorts the contents of a
text file, line by line. Sort is a standard command line program that print the
lines of its input or concatenation of all files listed in its argument list in
sorted order.
With -r switch, you
can sort the contents of any file in reverse order.
18.
vi Command –
The vi editor is a screen editor
which is available on almost all UNIX systems. In general, vi has two modes:
the command mode and the insert mode.
To begin entering text in an empty
file, you must first change from the command mode to the insert mode. To do
this, type the letter i. When you start typing, anything you type will
be entered into the file.
Type a few short lines and hit
Return at the end of each of line. Unlike word processors, vi does not
use word wrap. It will break a line at the edge of the screen. If you make a
mistake, you can use the Backspace key to remove your errors. If the Backspace
key doesn’t work properly on your system, try using the Ctrl h key combination.
19.
free Command –
free is a command which can give us
valuable information on available RAM in Linux machine. It also gives
information about total used and available space of physical memory and swap
memory with buffers used by kernel.
Free command with -t option,
will list the total line at the end.
20.
history Command –
One of the extensively used command
in Kali Linux is history command. The bash shell stores a history of
commands entered, which can be used to repeat commands by using the history
command.
In simple manner, you can run the history command by itself and will simply print out the bash history of current user to
the screen as shown below:












Shi h 👍👍👍👍
ReplyDeletePost a Comment